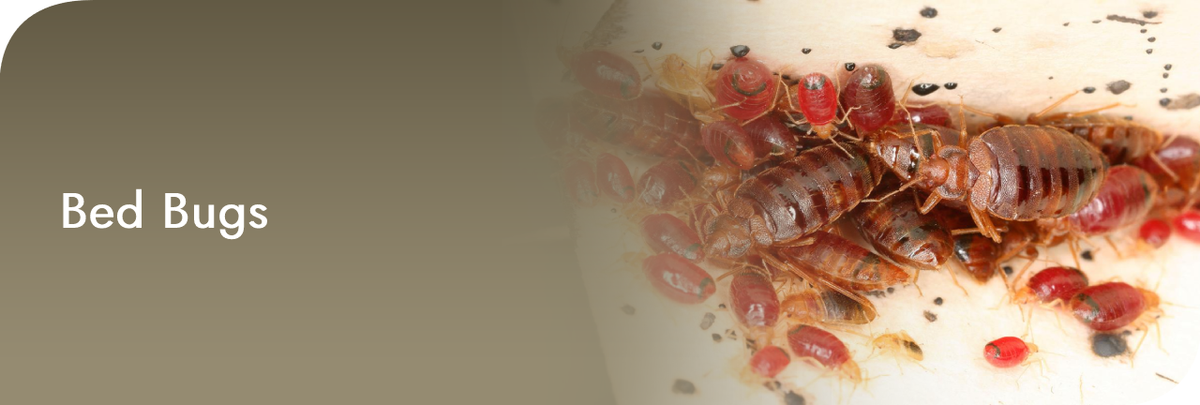
DO YOU KNOW? - THE BED BUGS
Bed bugs are a growing concern internationally and unlike cockroaches that love filthy environments, bed bugs are more common to be found in the nicest and cleanest homes and hotels as bed bugs are depending on only one factor, the food source – humans and pets. Bed bugs likely get their name from their habit of taking refuge in beds and feeding on humans while they sleep. Different from fleas, bed bugs don’t live on humans or pets, but they only live in the environment and they feed exclusively on human blood. But in an event where there is not enough human blood, they can bite the cats and dogs too (and any other animals). Bed bugs are not social insects, however, they tend to cluster together to seek for harbourage in small spaces like cracks and crevices.
Bed Bugs Biology
Bed bugs are oval in shape and only grow to about 5 – 7 mm in length. Prior to feeding, they are brown and flat. After feeding, they become redder in colour, swollen and elongated with human blood. Despite having reduced “wing pads,” bed bugs do not have wings and they cannot fly.
The Life Cycle
The common bed bug from the family Cimicidae (Cimex lectularius) has five developmental life stages. Each immature life stage (called nymphs or instars) depends on blood meals to moult their exoskeleton to grow larger. After growing through five instar moults, the bed bug becomes an adult. Adult bed bugs, both male and female, need regular blood meals to grow and reproduce. Each female can lay one to three eggs per day and 200 - 500 eggs per lifetime. The total development process from an egg to an adult can take place about 37 days at optimal temperature. Adult bed bugs have a life span of nearly one year depending on regular access to blood meals and favourable conditions.
Nymph - Immature phase of bed bug; eggs will hatch into nymphs, and nymphs will emerge into adults
Moult - The shedding of an outer layer or covering and the formation of its replacement
Exoskeleton - External covering of insects’ body (all arthropods have exoskeleton)
Bed Bugs Bite
Bed bugs are insects that are known for their scary bites during sleep as they are active during the night. Humans exhale carbon dioxide (CO2) the most during sleep, especially if the doors and windows are closed, and this attracts bed bugs to come out from their hiding areas and seek for human blood. What makes it worse is bed bugs can sense the exhaled CO2 as little as three feet away from the bed. Bed bugs don’t have teeth to bite, however they bite by piercing the skin using a thin, sharp mouth structure called stylet. When bed bugs bite, they excrete a tiny amount of anaesthetic to numb the skin so that the people are not aware of them being bitten.
Even though they are primarily active at night, if hungry they will seek for food sources even in the full daylight. Bed bugs feed only on blood and must have regular blood meals to survive and develop and they can take a blood meal seven times their own body weight in blood. However, bed bugs can live several months without a blood meal.
When Male Meets Female: The Trauma
Do you know that female bed bugs don’t have a genital opening? Bed bugs have a very unique mode of copulation termed traumatic insemination, whereby the male bed bug has sharp spines and pierces the female’s abdomen and deposits its sperm inside the female's body cavity to mate. This can damage the female reproductive system and reduce female life span. The female’s trauma in mating leads to male-avoidance behaviour and ultimately female dispersal, resulting in more areas to be infested by the bed bugs as the females are running away from the male bed bugs.
How To Find Bed Bugs?
Adult bed bugs are visible to the human eye and can be detected by sight, especially within mattress seams, bed frame and box springs. Bed bug nymphs can be harder to identify, as they are smaller in size and paler in colour. Bed bugs are great “hitch hikers,” they travel 5 - 20 feet from established hiding places (called harbourage) to feed on humans. They latch onto suitcases, clothes and linens and can end up wherever these items are taken.
When they are not feeding, bed bugs hide in a variety of places. Around the bed, they can be found near the piping, seams and tags of the mattress and box spring, and in cracks on the bed frame and headboard. If a room is heavily infested, bed bugs can also be found at:
In the seams of chairs and couches, between cushions, in the folds of curtains
In drawer joints
In electrical receptacles and appliances
Under loose wallpaper and wall hangings.
At the junction where the wall and the ceiling meet
How To Control Bed Bugs?
There are several ways that can be carried out if your place is infested with bed bugs. However, the best way to control bed bugs (and any pests) would be to have a comprehensive approach – Integrated Pest Management (IPM) technique.
IPM is a technique that combines the biological, physical and chemical approaches to control insect pests.
Identify the pest
Be sure of the type of pest you’re facing, as different pests will have different control approaches. Compare your insect with a pest picture online, or seek for any professional pest expert to help you identify the pest. Look for any bed bugs signs – (i) live or dead bed bugs, (ii) small, yellowish shed skins, (iii) black and rusty spots which are blood stains and their droppings.
Identify the infested areas
Identify the infested areas and don’t throw away your infested sofas and mattresses as things can be treated and saved. Throwing up your infested furniture can be more expensive as the bed bugs might spread to other areas (and other homes too) and cause more headaches.
Bed bugs removal
Remove and wash the bed sheets, blankets and clothings if your bed is infested with bed bugs. Simply place the bed sheets, blankets and clothings in a sealed plastic bag during transportation to ensure the bed bugs won’t disperse to other areas. Carefully vacuum the floors, carpets, furniture, bed frames and all cracks and crevices around the infested areas and immediately place the used vacuum bag in a sealed plastic bag and throw it in an outside garbage bin.
Wash and heat-dry
Regularly wash and heat-dry your bed sheets, blankets and clothings. Heat-dry is important as bed bugs and their eggs can only be killed at a high temperature (60°C).
Chemical treatment
Use insecticide to control bed bugs. To control bed bugs, it is important to use insecticide that works to kill all stages including the eggs with the lowest risk to humans, pets and the environment such as natural insecticides. There are several natural insecticides available in the market that really work for bed bugs such as EcoRaider.
Turn to professionals, if needed
If you don’t really know or are confident about what to do to control bed bugs, it is highly recommended to seek a professional pest expert. Seek for pest experts with good reputations and request them to use an IPM approach and a low risk insecticide. This is important to ensure that the bed bugs are eliminated with the slightest impact to human health, pets and the environment.